Introduction
Large Language Models (LLMs) are Artificial Intelligence algorithms that use massive data sets to summarize, generate and reason about new content. LLMs are built on a set of neural networks based on the transformer architecture. Each transformer consists of encoders and decoders that can understand text sequence and the relationship between words and phrases in it.
The generative AI technologies that have been enabled by LLMs have transformed how organizations serve their customers, how workers perform their jobs and how users perform daily tasks when searching for information and leveraging intelligent systems. To build an LLM we need to define the objective of the model and whether it will be chatbot, code generator or a summarizer.
Building an LLM
Building an LLM requires the curation of vast datasets that enable the model to gain a deep understanding of the language, vocabulary and context around the model’s objective. These datasets can span terabytes of data and can be grown even further depending on the model’s objectives [1].
Data collection and processing
Once the model objectives are defined, data can be gathered from sources on the internet, books and academic literature, social media and public and private databases. The data is then curated to remove any low-quality, duplicate or irrelevant content. It is also important to ensure that all ethics, copyright and bias issues are addressed since those areas can become of major concern as the model develops and begins to produce the results and predictions it is designed to do.
Selecting the model architecture
Model selection involves selecting the neural network design that is best suited for the LLM goals and objectives. The type of architecture to select depends on the tasks the LLM must support, whether it is generation, translation or summarization.
- Perceptrons and feed-forward networks: Perceptrons are the most basic neural networks consisting of only input and output layers, with no hidden layers. Perceptrons are most suitable for solving linear problems with binary output. Feed-forward networks may include one or more layers hidden between the input and output. They introduce non-linearity, allowing for more complex relationships in data [2].
- Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs): RNNs are neural networks that process information sequentially by maintaining a hidden state that is updated as each element in the sequence is processed. RNNs are limited in capturing dependencies between elements within long sequences due to the vanishing gradient problem, where the influence of distant input makes it difficult to train the model as their signal becomes weaker.
- Transformers: Transformers apply global self-attention that allows each token to refer to any other token, regardless of distance. Additionally, by taking advantage of parallelization, transformers introduce features such as scalability, language understanding, deep reasoning and fluent text generation to LLMs that were never possible with RNNs. It is recommended to start with a robust architecture such as transformers as this will maximize performance and training efficiency.
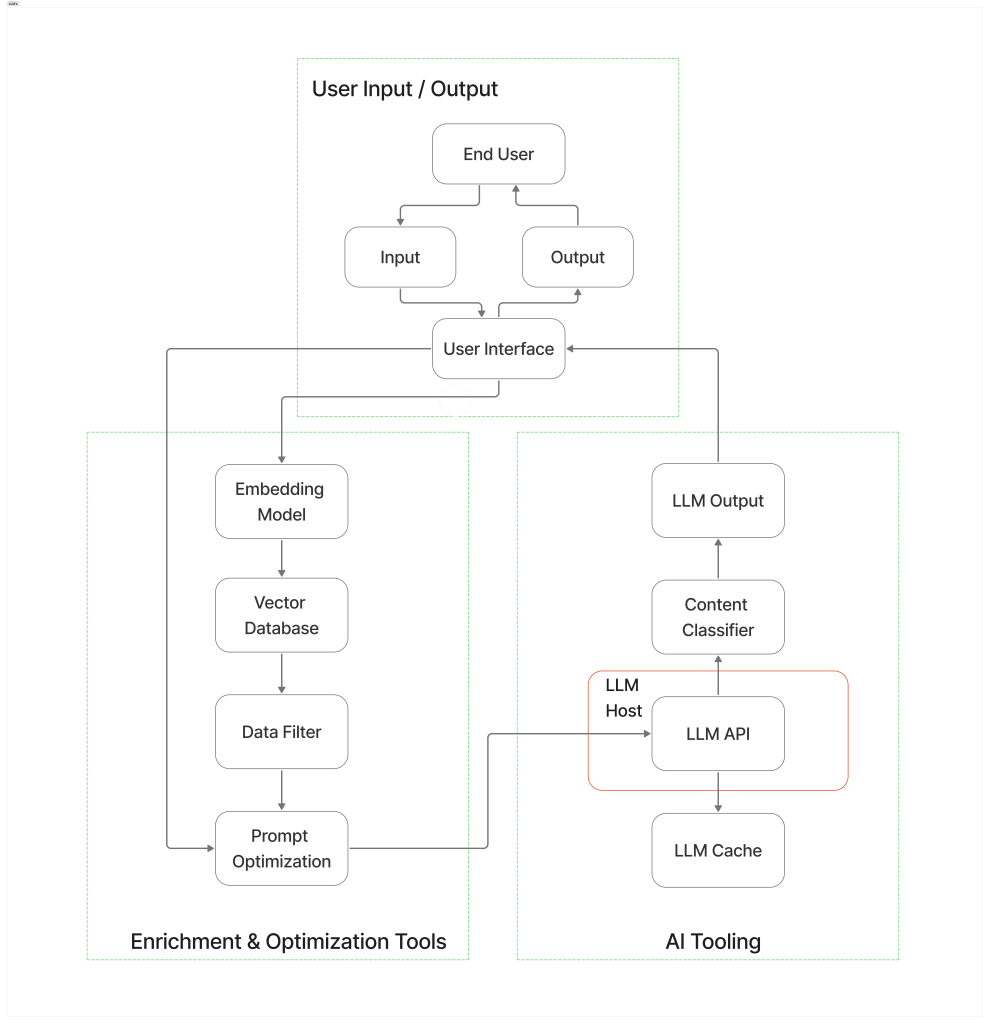
Implementing the model
Implementing the model requires using a deep learning framework such as TensorFlow or PyTorch to design and assemble the model’s core architecture [4]. The key steps in implementing the model are:
- Defining the model architecture such as transformers and specifying the key parameters including the number of heads and layers.
- Implementing the model by building the encoder and decoder layers, the attention mechanisms, feed-forward networks and normalizing the layers.
- Designing input/output mechanisms that enable tokenized text input and output layers for predicted tokens.
- Using modular design and optimizing resource allocation to scale training for large datasets.
Training the model
Model training is a multi-phase process requiring extensive data and computational resources. These phases include:
- Self-supervised learning where the model is fed massive amounts of data, so that it can be trained in language understanding and predicting missing words in a sequence.
- Supervised learning where the model is trained to understand prompts and instructions allowing it to generalize, interact and follow detailed requests.
- Reinforcement learning with Human Feedback (RLHF) involves learning with human input to ensure that output matches human expectations and desired behaviour. This also ensures that the model avoids bias and harmful responses and that the output is helpful and accurate.
Fine tuning and customization
Customization techniques include full model fine-tuning where all weights in the model are adjusted to focus on task-specific data. It is also possible to fine-tune parameters and engineer prompts to focus on smaller modules, saving resources and enabling easier deployment.
Training a pre-trained model based on domain-specific datasets allows the model to specialize on target tasks. This is easier and less resource-intensive than training a model from scratch since it leverages the base knowledge already learned by the model.
Model deployment
Deploying the LLM makes it available for real-world use, enabling users to interact with it. The model is deployed on local servers or cloud platforms using APIs to allow other applications or systems to interface with it. The model is scaled across multiple GPUs to handle the growing usage and improve performance [5]. The model is continually monitored, updated and maintained to ensure it remains current and accurate.
Ethical and legal considerations
The ethical and legal considerations are important in the development and deployment of LLMs. It is important that the LLM is unbiased and that it avoids propagating unfair and discriminatory outputs. This extends to discriminatory and harmful content which can be mitigated through reinforcement learning with human feedback (RLHF).
Training data may contain sensitive and private information, and the larger the datasets used to train the model the greater the privacy risks they involve. It is essential that privacy laws are adhered to and followed to ensure the models can continue to evolve and develop while preventing unintended memorization or leakage of private information.
Copyright and intellectual property must also be protected by ensuring that the proper licenses are obtained. Regular risk and compliance assessments and proper governance and oversight over the model life cycle can help mitigate ethical and legal issues.
Conclusion
Developing and deploying an LLM in 2025 requires a combination technical, analytical and soft skills. Strong programming skills in Python, R and Java are critical to AI development. A deep understanding of machine learning and LLM architectures including an understanding of the foundational mathematical concepts underlying them, are also critical. It is also important to have a good understanding of hardware architectures including CPUs, GPUs, TPUs and NPUs to ensure that the tasks performed by the LLM are deployed on the most suitable hardware to ensure efficiency, scalability and cost-effectiveness.
Other skills related to data management, problem-solving, critical thinking, communication and collaboration, and ethics and responsible AI are also essential in ensuring the models remain useful and sustainable.
References
[1] The Ultimate Guide to Building Large Language Models
[2] Feedforward Neural Networks
[3] The architecture of today’s LLM applications
[4] How to Build a Large Language Model: A Comprehensive Guide